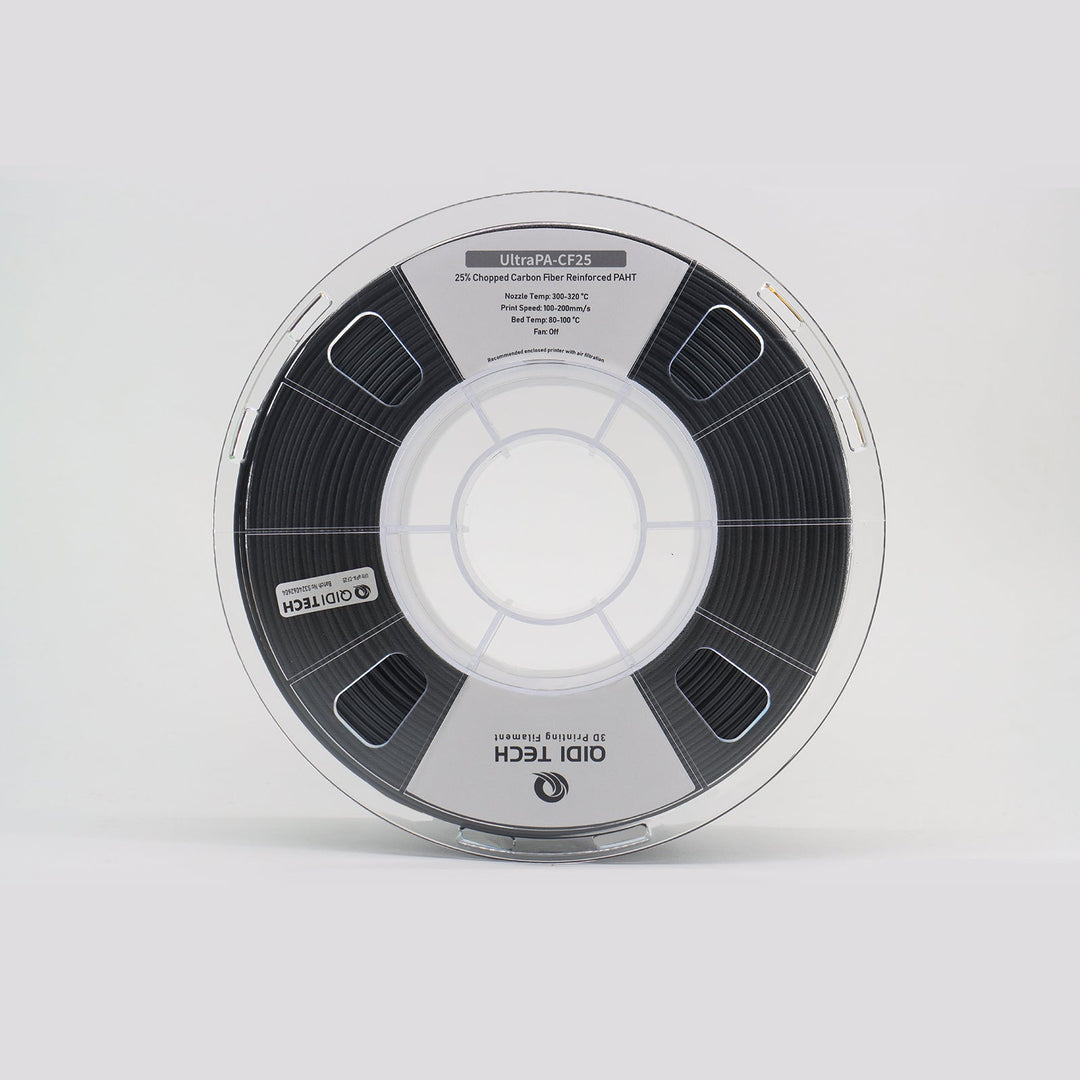

Ultrapa-CF25 (PPA-CF πυρήνα) νήμα)
Χαρακτηριστικά προϊόντος
- Εξαιρετικές μηχανικές ιδιότητες
- Υψηλή διαστατική σταθερότητα
- Εξαιρετική θερμική αντίσταση
- Εξαιρετική πρόσφυση στρώσεων
Προφυλάξεις κατά τη χρήση
Ακροφύσιο 0,2 mm Μη συμβατό
Πρέπει να στεγνώσει πριν από τη χρήση για να επιτευχθεί βέλτιστη ποιότητα εκτύπωσης
- Σε απόθεμα, έτοιμο για αποστολή
- Backrorder, αποστολή σύντομα
Οι τιμές αποστολής ποικίλλουν ανάλογα με την τοποθεσία. Δείτε τα προϊόντα μας. Πολιτική αποστολής για λεπτομέρειες.
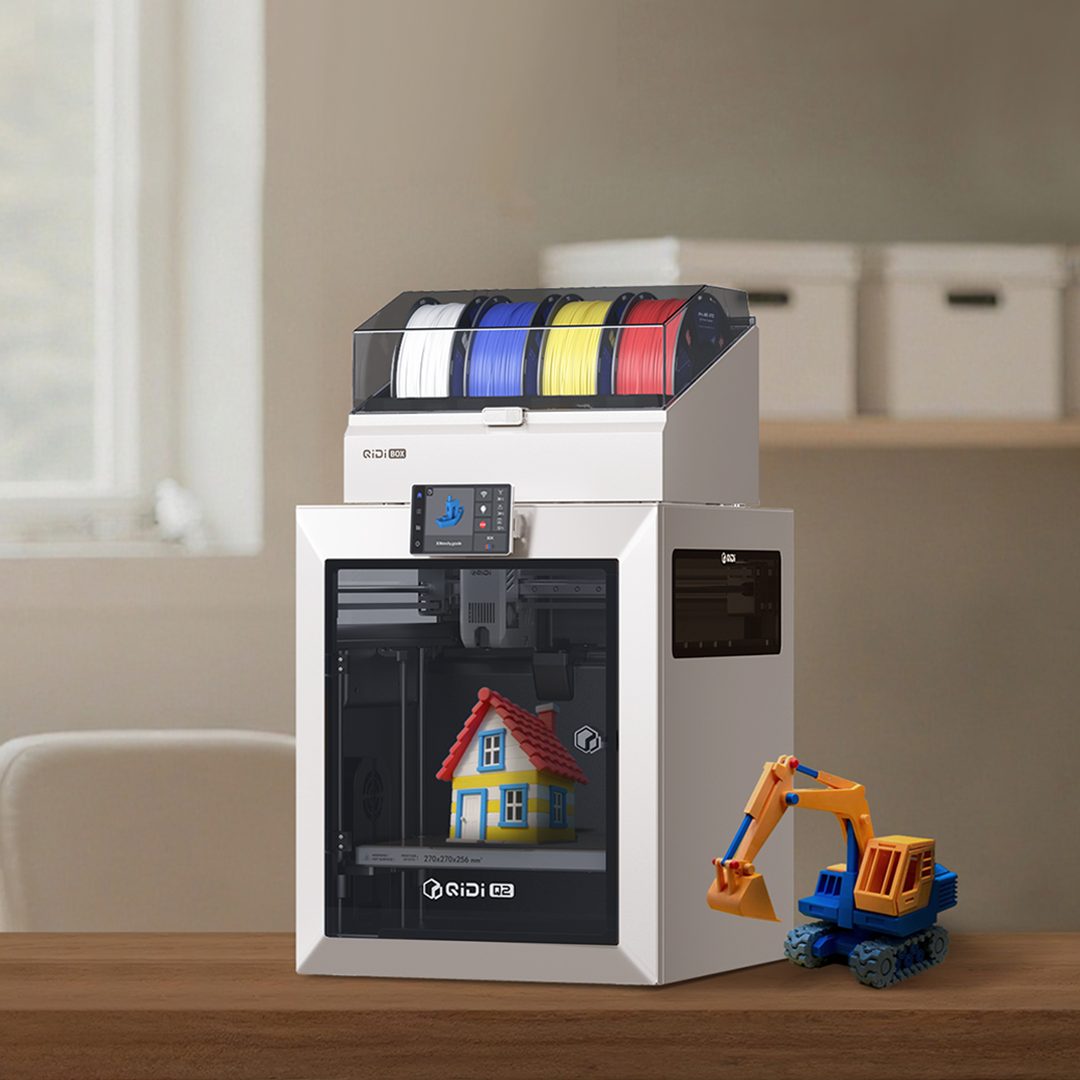

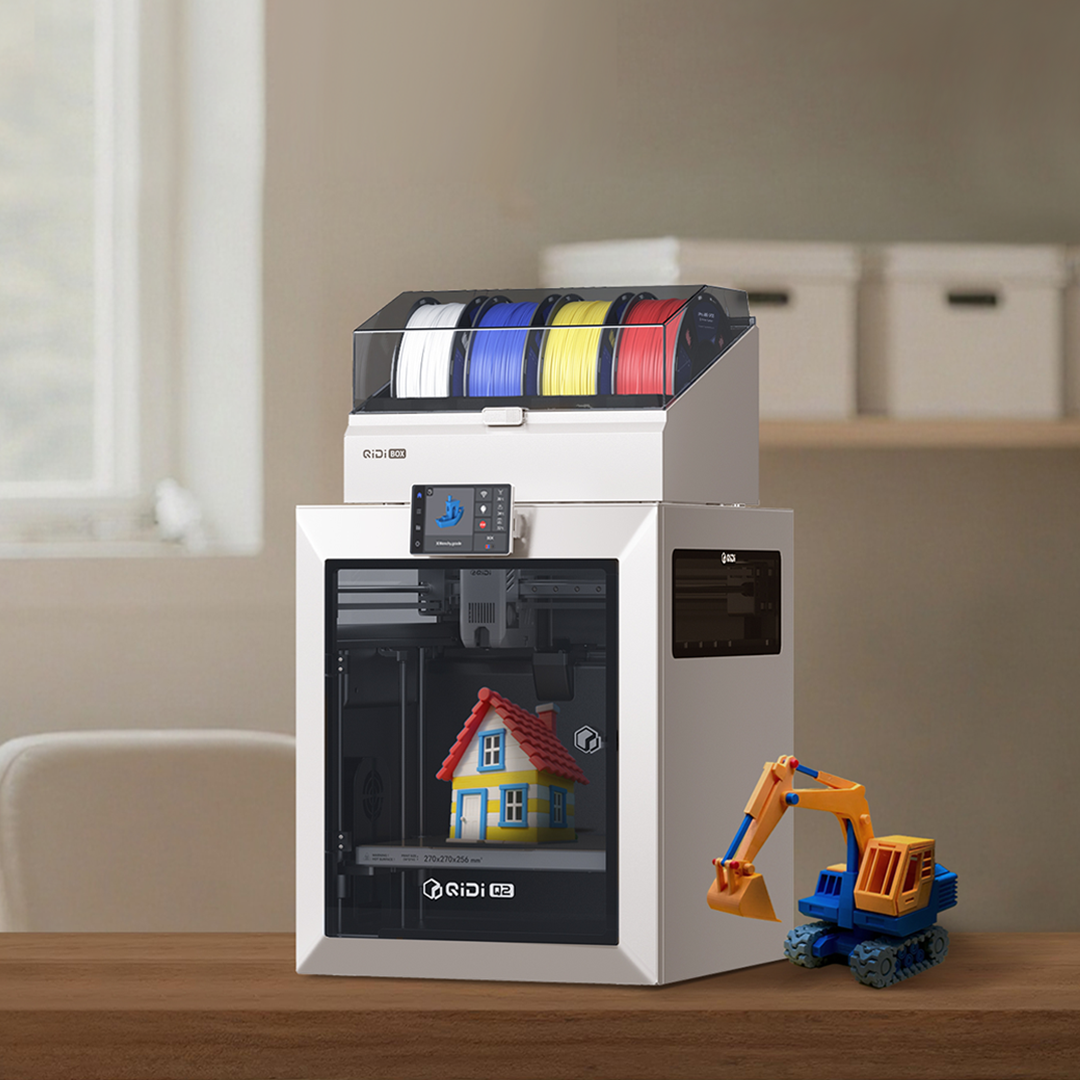
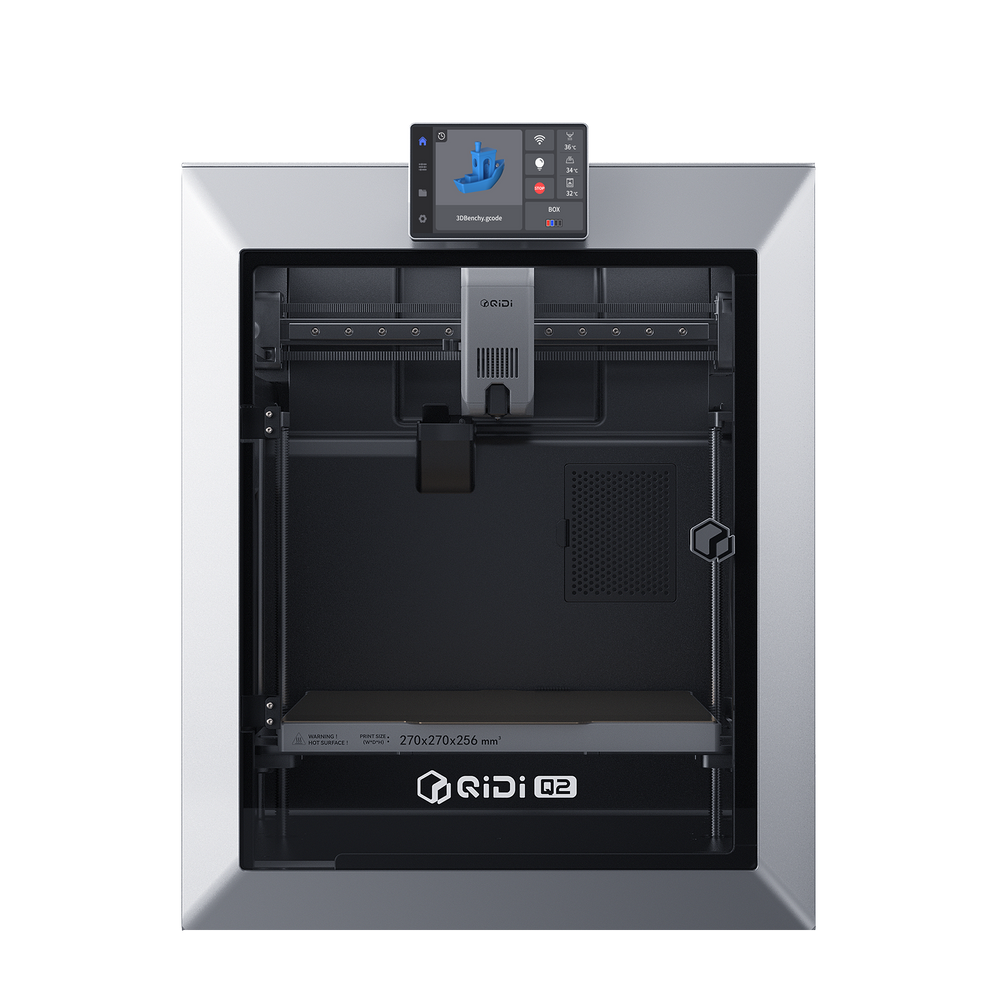
 Q2
Q2
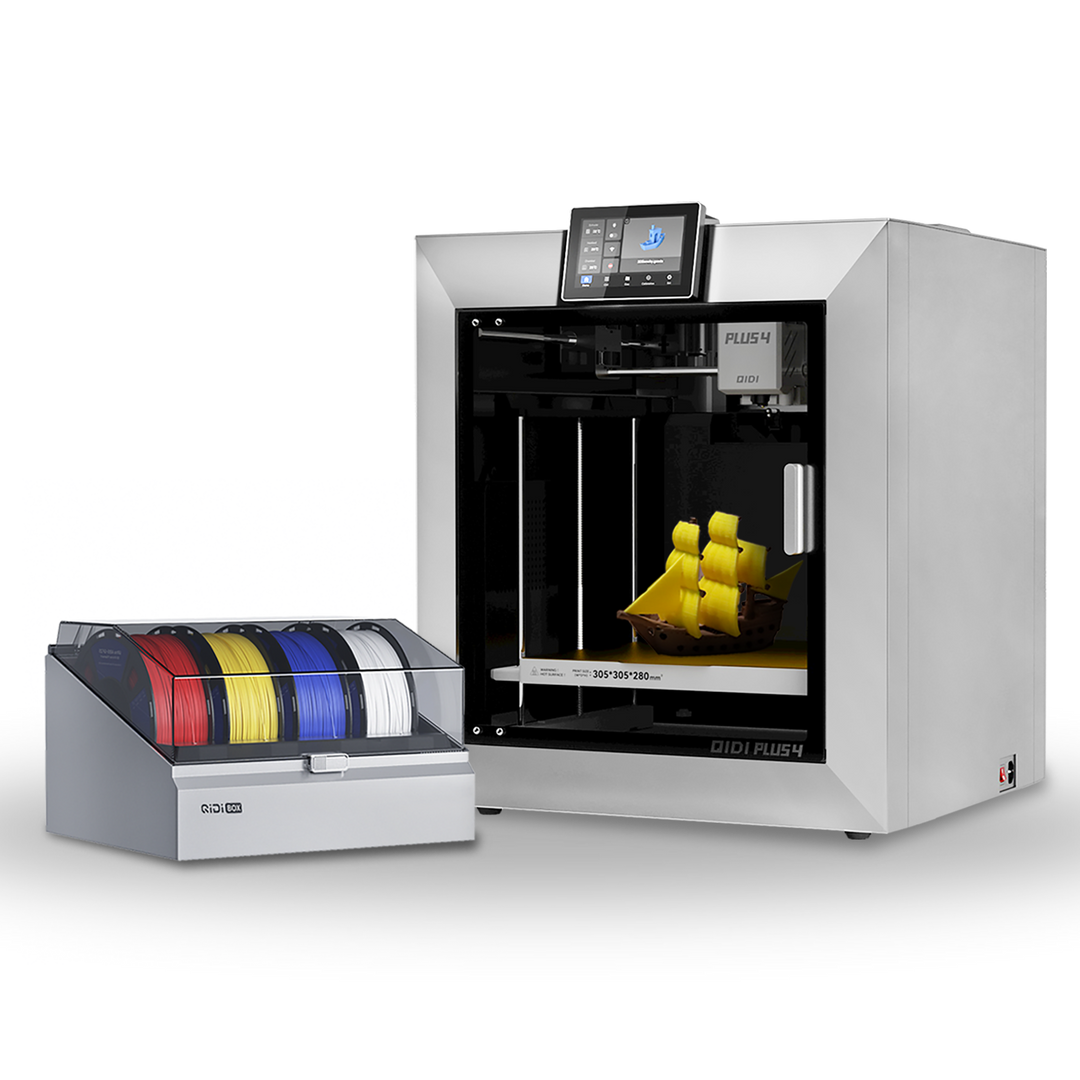
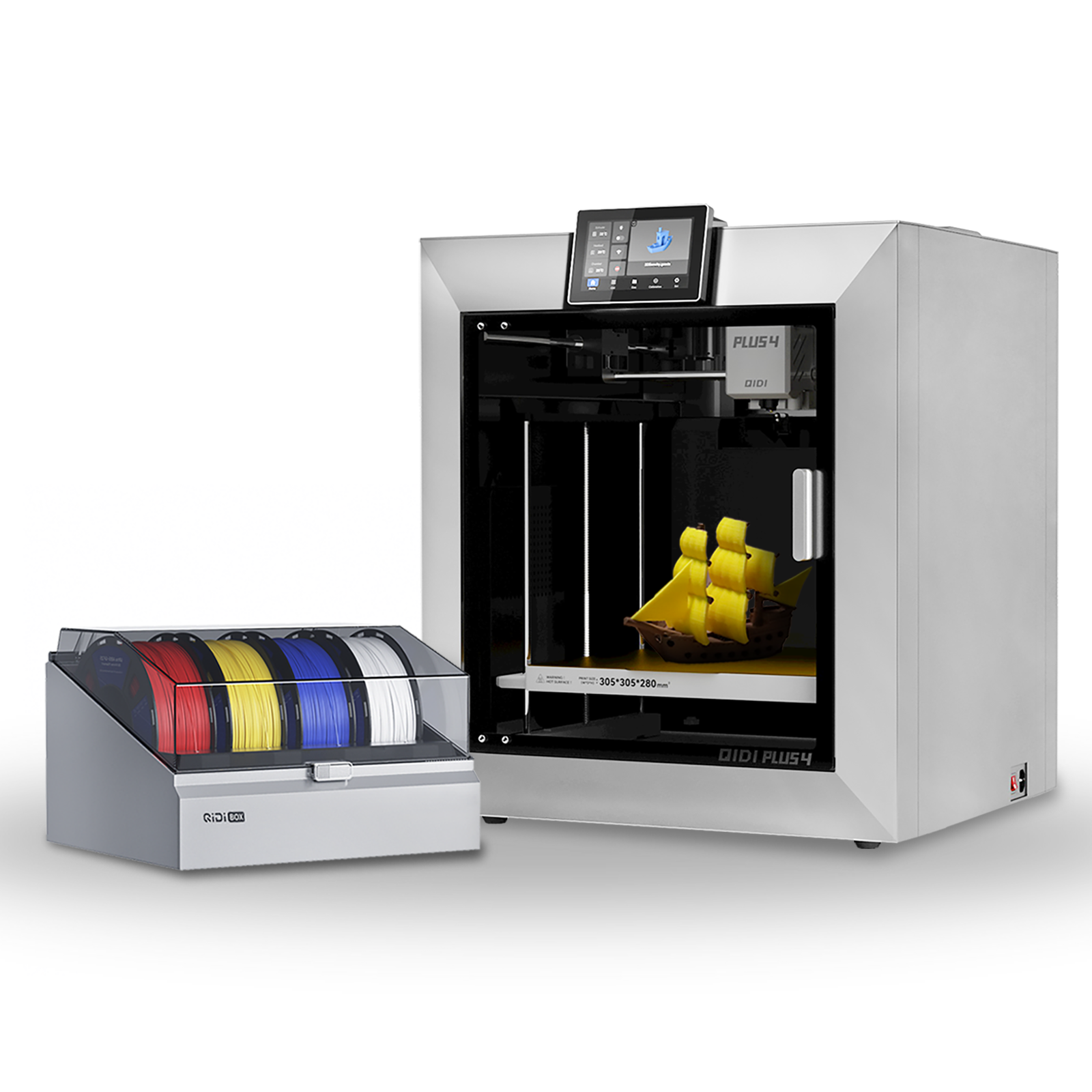 Plus4
Plus4
 Κουτί QIDI
Κουτί QIDI
![[Qidi X-CF Pro, speziell für den Druck von Kohlefaser und Nylon entwickelt] - [QIDI Online Shop DE]](http://eu.qidi3d.com/cdn/shop/files/3034a1133efe01daba919094b70c6310.jpg?v=1750300120) Q1Pro
Q1Pro
![[Qidi X-CF Pro, speziell für den Druck von Kohlefaser und Nylon entwickelt] - [QIDI Online Shop DE]](http://eu.qidi3d.com/cdn/shop/products/X-MAX3-3D-Printer-02.png?v=1750300138) Max3
Max3
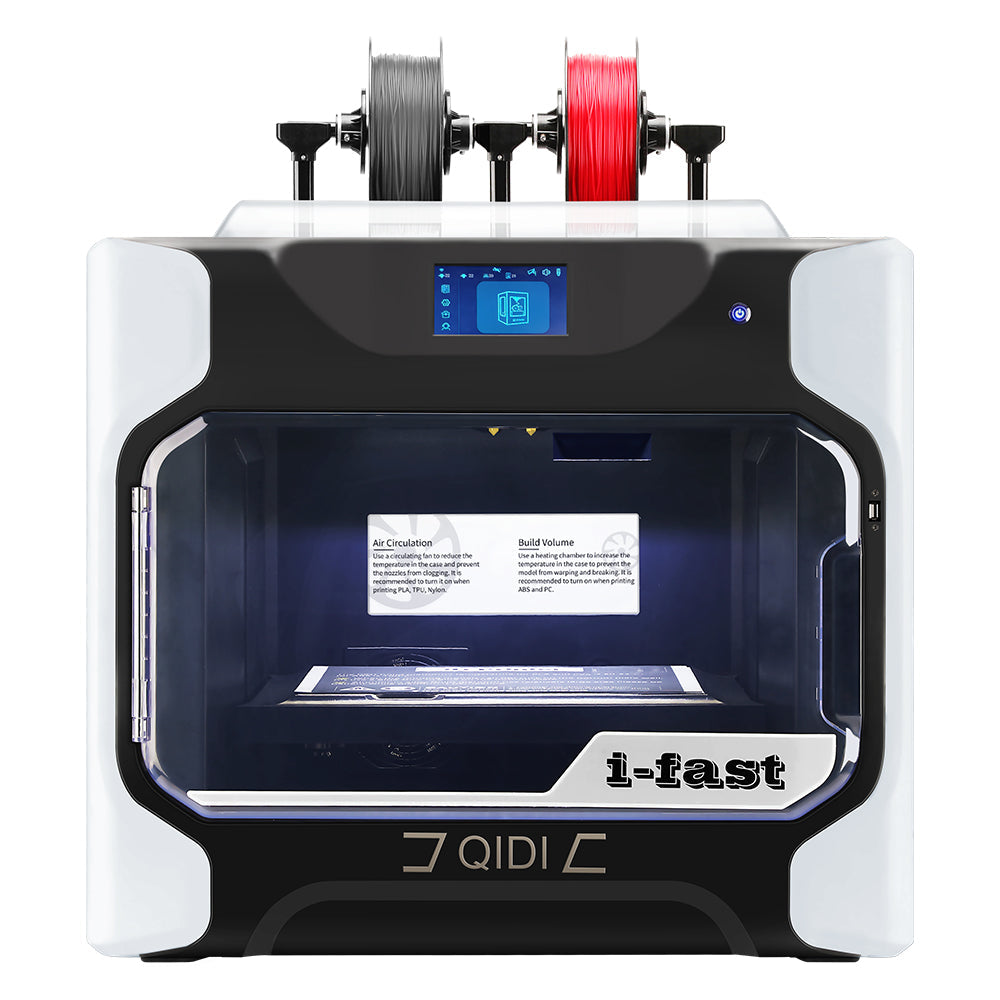 I-Fast
I-Fast















![[Qidi X-CF Pro, speziell für den Druck von Kohlefaser und Nylon entwickelt] - [QIDI Online Shop DE]](http://eu.qidi3d.com/cdn/shop/products/X-MAX3-3D-Printer-02.png?v=1750300138&width=1080)
