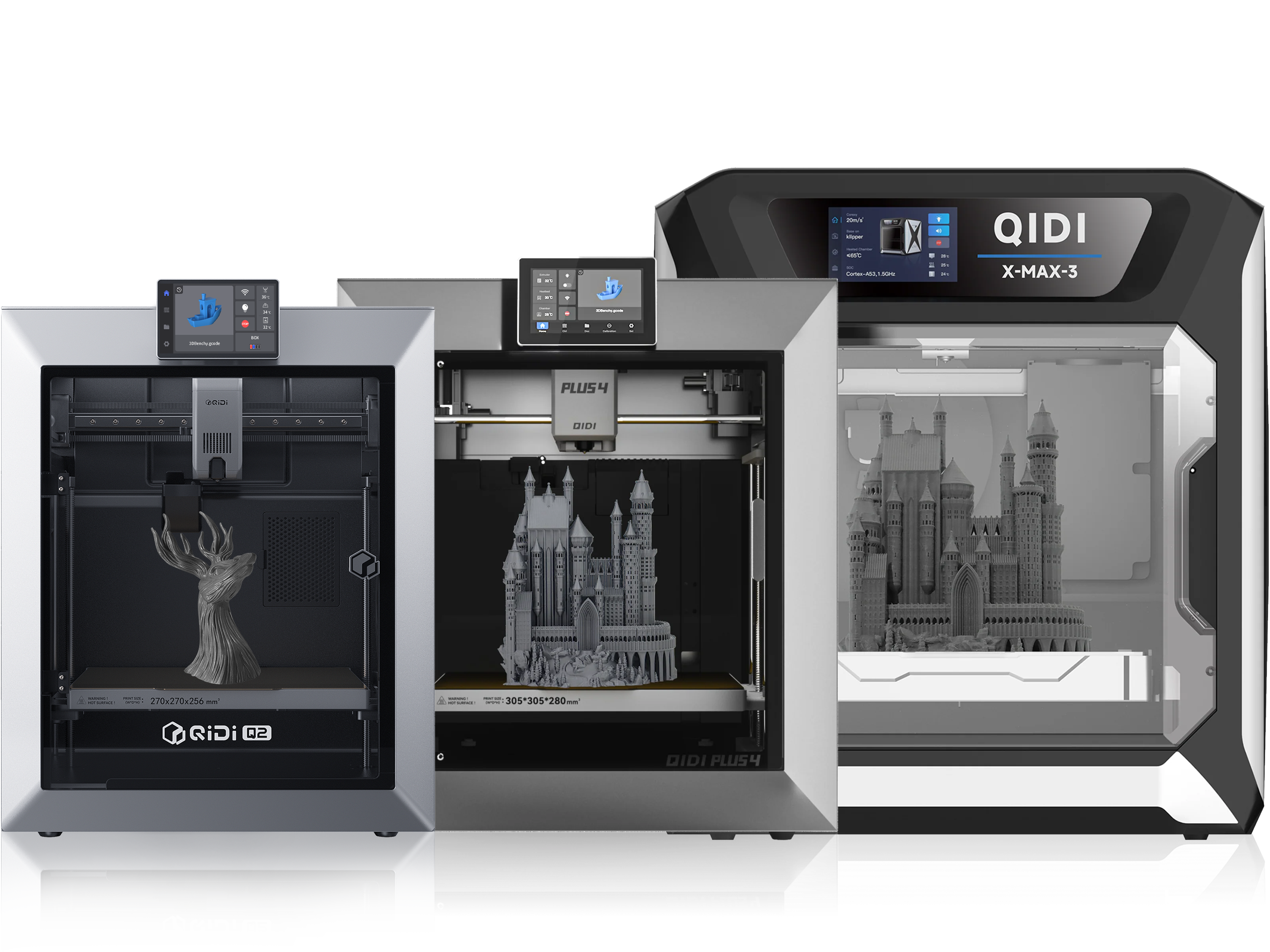
Guida all'acquisto di stampanti 3D
Trova il 3D perfetto
stampante per i tuoi progetti.
Inizia oggi stesso la tua avventura creativa!
Dai vita alle tue idee con <tc>QIDI</tc> Stampanti 3D FDM
La modellazione a deposizione fusa (FDM) è una tecnologia di stampa 3D diffusa al centro di
Le stampanti FDM sono tra le tipologie di stampanti 3D più diffuse oggi sul mercato. Questo tipo di stampante 3D offre un'ottima compatibilità con i materiali e applicazioni intuitive.
Versatilità dei materiali: Le stampanti 3D FDM supportano l'uso di una varietà di materiali termoplastici, tra cui
Rapporto costo-efficacia: Rispetto ad altri metodi di stampa 3D, la tecnologia FDM è generalmente più conveniente. Il costo delle stampanti FDM è relativamente basso e anche il prezzo delle materie prime (filamenti) è ragionevole. Questo rende la FDM una scelta valida per hobbisti, insegnanti e piccole e medie imprese.
Facile da usare e da manutenere: Le nostre stampanti FDM sono dotate di un pannello di controllo semplice e intuitivo, che consente ai principianti di controllare facilmente le funzioni di base della stampante premendo pulsanti o ruotando le manopole. Il funzionamento è intuitivo e di facile comprensione. Anche la manutenzione è semplice, e prevede principalmente la pulizia regolare, la sostituzione degli ugelli e la calibrazione occasionale.
Le stampanti 3D FDM sono utilizzate in molti campi, tra cui:
Necessità quotidiane: Stampa articoli per la casa come portacellulari, portachiavi, sottobicchieri, portaspezie e forniture per ufficio come contenitori per documenti e tappetini per mouse.
Pezzi artistici e decorativi: Utilizzato per creare sculture, tra cui sculture astratte e sculture con temi specifici, e per realizzare gioielli unici come orecchini e pendenti per collane.
Modelli educativi: Creare modelli didattici, come modelli di organi umani nelle lezioni di biologia, modelli topografici nelle lezioni di geografia e modelli geometrici nelle lezioni di matematica.
Prototipi industriali & Parti personalizzate: Stampa prototipi di prodotti per testarne l'aspetto e la funzionalità nelle prime fasi di sviluppo del prodotto e stampa parti personalizzate per attrezzature industriali speciali.
Medico & Applicazioni sanitarie: Realizzare apparecchi ortopedici personalizzati, come cuscinetti di supporto per l'arco plantare e guide chirurgiche per supportare la chirurgia orale o ortopedica.
Se non sei sicuro di quale stampante 3D sia adatta a te, puoi prima chiarire lo scopo o l'obiettivo della stampa:
Scopo di stampa
Livello del consumatore (personale/familiare): adatto per la stampa di piccoli modelli, progetti creativi e solitamente con un budget inferiore, come
Livello professionale (istruzione/laboratorio): deve tenere conto sia della precisione che della stabilità, il che supporta la stampa ad alta velocità e il livellamento automatico.
Industriale (produzione/manifatturiero) stampanti come la
Target di stampa
Dimensioni del modello: Il livello industriale richiede grandi dimensioni di costruzione, mentre il livello consumer è in genere di 200-300 mm³.
Compatibilità dei materiali: Se hai bisogno di stampare materie plastiche tecniche (
È anche possibile analizzare parametri prestazionali come la precisione di stampa. La precisione di stampa è misurata da fattori quali l'altezza dello strato e il diametro dell'ugello. Altezze dello strato e diametri dell'ugello inferiori generalmente producono stampe a risoluzione più elevata con dettagli più fini. Se il progetto richiede parti ad alta precisione, è consigliabile cercare una stampante in grado di raggiungere altezze dello strato inferiori e con ugelli più piccoli.
Domande frequenti
Trova le risposte alle tue domande più urgenti sulle nostre macchine e servizi di stampa 3D.
Una stampante 3D FDM, nota anche come stampanti Fused Deposition Modeling, è una stampante che crea oggetti attraverso la deposizione strato per strato di filamento di plastica fusa. Il filamento plastico viene riscaldato fino a quando non diventa fuso ed estruso attraverso un ugello per formare la forma di interesse. Uno dei motivi per cui le stampanti FDM sono popolari è che sono economiche e molto facili da usare, quindi sono ampiamente utilizzate sia dai principianti che dagli utenti professionisti.
Le stampanti 3D FDM presentano diversi vantaggi. Il primo è che sono solitamente più convenienti rispetto ad altre tecnologie di stampa 3D. Questa economicità le rende accessibili a un vasto mercato, come hobbisti, insegnanti e professionisti. In secondo luogo, le stampanti FDM sono facili da usare e supportano un'ampia gamma di materiali, dai termoplastici resistenti a quelli di qualità ingegneristica, come
Il processo di stampa 3D FDM prevede la progettazione di un modello 3D utilizzando un software CAD. Una volta che il progetto è pronto, viene utilizzato il software di slicing per convertire il modello in vari livelli. La stampante poi riscalda il filamento plastico e lo estrude attraverso un ugello, stendendo ogni strato secondo il modello affettato. Man mano che lo strato viene steso, si raffredda e si solidifica, costruendo l'oggetto finale. Questo meccanismo strato per strato fornisce il controllo sulla forma e sulla struttura dell'oggetto finale.
SLA e FDM sono due diverse tecnologie di stampa 3D. La differenza principale è il materiale e il processo. Le stampanti FDM utilizzano filamenti termoplastici, che vengono fusi ed estrusi per stendere gli strati. Le stampanti SLA utilizzano resina liquida polimerizzata da un laser per polimerizzare ogni strato. La SLA ha solitamente una risoluzione migliore e le superfici sono più lisce, quindi è molto adatta per progetti con molti dettagli e molto complessi. La tecnologia FDM è più adatta per prototipi funzionali e parti più grandi perché è più resistente ed economica. In generale, la FDM è anche più economica rispetto alle stampanti SLA e ai loro materiali.
La risoluzione di stampa, l'altezza dello strato, la temperatura dell'estrusore e della piattaforma, la velocità di stampa, la qualità del filamento, la dimensione dell'ugello e le impostazioni corrette dell'affettatrice influiscono tutti sulla qualità di stampa finale. La doppia estrusione, una camera di costruzione chiusa e le funzionalità di calibrazione automatica contribuiscono inoltre a migliorare coerenza, precisione e affidabilità.






![[Qidi X-CF Pro, speziell für den Druck von Kohlefaser und Nylon entwickelt] - [QIDI Online Shop DE]](http://eu.qidi3d.com/cdn/shop/products/X-MAX3-3D-Printer-02.png?v=1763120465)